Welded Spiral Steel Pipes – GOST 8696
September 23, 2023
What is a reducer in piping, How to select reducer?
September 30, 2023Abstract
This doctoral thesis presents a comprehensive study of stainless steel heat exchanger U pipes, their manufacturing processes, mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and thermal performance. The study aims to understand the critical factors influencing the performance of U pipes in heat exchangers and propose strategies to enhance their efficiency and lifespan.
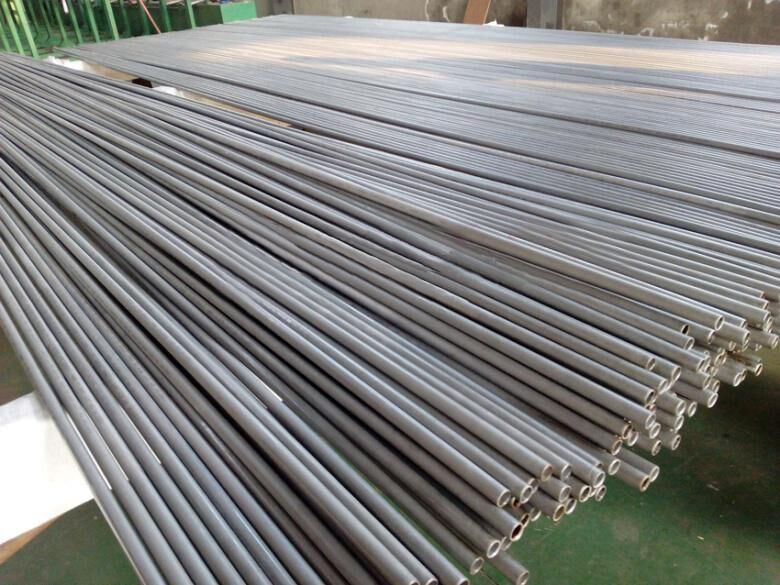
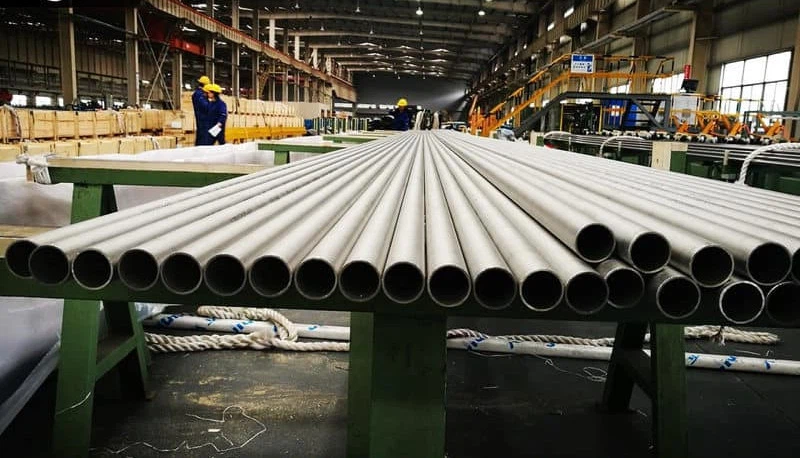
ASTM A213 Stainless Steel Seamless U Tube
Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger Tube
Stainless Steel Reheater Tube
Products Specification:
Basic specification
●Welded: A249, A269, A789
●Seamless: A213, A269, A789
●Grades: TP304 / 304L, TP316 / TP316L, TP321 / TP321H, 2205 / S31803, TP310S.
●Surface: Annealing, bright annealing, polishing
●Outside diameter: 6.53 mm – 127 mm
●Thickness: 0.5 mm – 5 mm
●Tolerance: +/-0.05 mm
●Application: Heat exchanger, boiler, condenser, cooling, heating
Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger Tube
Technical Requirements:
Straight Tubes Standard Specification For Bending:
ASME SA 213; ASME SB 163; ASME A789, ASME SA268, ASME SA269, etc.
Marking: Before Bending By Marking Machine All Over The Tube Length (Bent Section After Heat
Treatment Without Marking)
Note: Marking is also possible After Bending On The Straight Parts Of U-Bending Tube.
U-Bend Tubes:
-TEMA RCB 2.31 Standard Of The Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association (9th Edition).
-ASTM A688/ASME SA688 Standard Specification For Welded Tubes Of Austenitic Corrosion Resistant
Steel Grade Designed For Feed Water Boilers.
-ASTM B163/ASME SA163 Standard Techinical Requirements For Tubes Of Nickel And Nickel Alloy For
Condensers And Heat Exchangers.
-Customer Specifications.
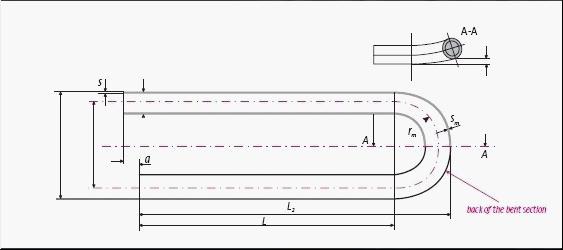
Bending Radius: From 1.5*OD(Outside Diameter) To 1500mm
When Ordering Tubes With Radius less or equal to 1.5*OD, It Is Necessary To Agree Precision Of Geometrics.
Straight Tubes Maximum Length:(Before Bending): 35000 mm.
Leg Length: Min 1 Meter, Max. 16500 mm (For Max R=1500mm)
Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter sets the context for the study, discussing the role of heat exchangers in various industries and the importance of U pipes in the design of these heat exchangers. It also outlines the research objectives and the scope of the study.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
This chapter reviews existing studies on heat exchanger U pipes, focusing on materials used, manufacturing processes, and factors affecting their performance. It identifies gaps in the current knowledge and research, setting the stage for the present study.
Chapter 3: Materials and Manufacturing Processes
This chapter delves into the details of stainless steel as a material for manufacturing U pipes, discussing its mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It also covers the manufacturing processes used to form U pipes, including bending techniques and heat treatment processes.
Chapter 4: Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel U Pipes
This chapter presents an in-depth analysis of the mechanical properties of stainless steel U pipes, including tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and hardness. It discusses how these properties influence the performance of U pipes in a heat exchanger, and how they can be enhanced through various heat treatment processes.
Chapter 5: Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steel U Pipes
This chapter evaluates the corrosion resistance of stainless steel U pipes, examining how different environments (such as seawater, acidic conditions, and high-temperature operations) affect their corrosion behavior. It also explores strategies to improve the corrosion resistance of these pipes.
Chapter 6: Thermal Performance of Stainless Steel U Pipes
This chapter investigates the thermal performance of stainless steel U pipes in a heat exchanger, examining factors such as heat transfer coefficient, pressure drop, and overall heat transfer rate. It also proposes strategies to enhance the thermal performance of these pipes.
Chapter 7: Case Studies
This chapter presents several case studies where stainless steel U pipes are used in heat exchangers in different industries, such as power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC. It discusses the challenges encountered and the solutions implemented to improve their performance.
Chapter 8: Conclusions and Recommendations
This chapter summarizes the key findings of the study, drawing conclusions about the performance of stainless steel U pipes in heat exchangers and suggesting recommendations for future research.
Chapter 9: References
This chapter lists all the references cited in the thesis, following the appropriate citation style.
Chapter 10: Appendices
This chapter includes any supplementary information, such as detailed calculations, additional data, and graphical representations, that support the research but are too detailed for inclusion in the main text.
As the demand for energy-efficient systems increases, the need to understand and improve the performance of heat exchangers becomes more critical. This study contributes to the body of knowledge in this area by providing an in-depth analysis of stainless steel heat exchanger U pipes, offering valuable insights for researchers, engineers, and industry professionals.













